Archaea
Most archaeans don’t look that different from bacteria under the microscope. The extreme conditions under which most species of archaea live has made them difficult to culture, so their unique place among living organisms long went unrecognized. However, biochemically and genetically, they are as different from bacteria as you are. They are not Bacteria, they are Archaea.
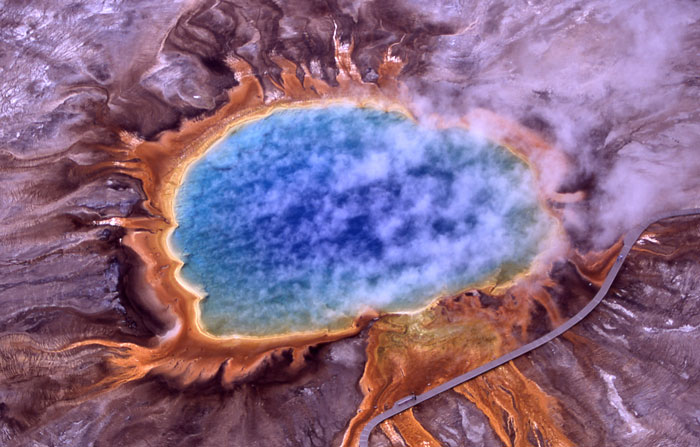
Figure 3.20: Archaea were first detected in extreme environments, such as hot springs like Grand Prismatic Spring in Yellowstone National Park. Archaea were initially viewed as extremophiles that exist only in habitats such as hot springs and salt lakes. By the end of the 20th century, microbiologists realized that the archaea are common in much less extreme habitats, such as soils and oceans.
Image from URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archaea
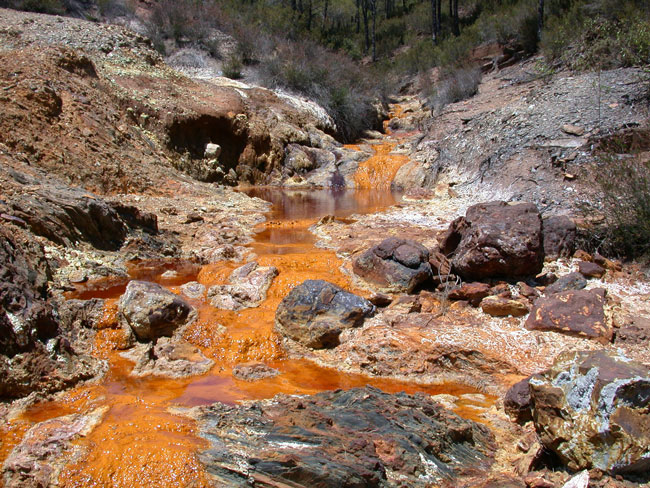

Figure 3.21: A new group of archaea were recently discovered in acid rock drainage (sometimes referred to as acid mine drainage), like this acid drainage seen in the Rio Tinto River in Spain.
Image from URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archaea
A recent study of the microbial species diversity found in prairie, desert and rainforest soils suggests that there may be more archaea and fungi species in soils than there are bacterial species, as discussed in this article, “New Study Suggests Many Unknown Microbes in Soil“, from Science Daily. Most of the soil archaea that have been found to date have been impossible to cultivate (grow) in a lab, and so we do not have good images of these amazing life forms.