The Tree of Life
The phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species. In a phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the most recent common ancestor of the descendants. Each node is called a taxonomic unit.
Key Concept: All cells come from preexisting cells.
Most broadly, scientists classify life into three domains. Humans, along with all animals and many other types of life, belong to the domain Eucarya (sometimes spelled Eukarya). The domain Eucarya contains eukaryotes that can be further classified into four kingdoms: Plantae, Fungi, Animalia, and Protista.
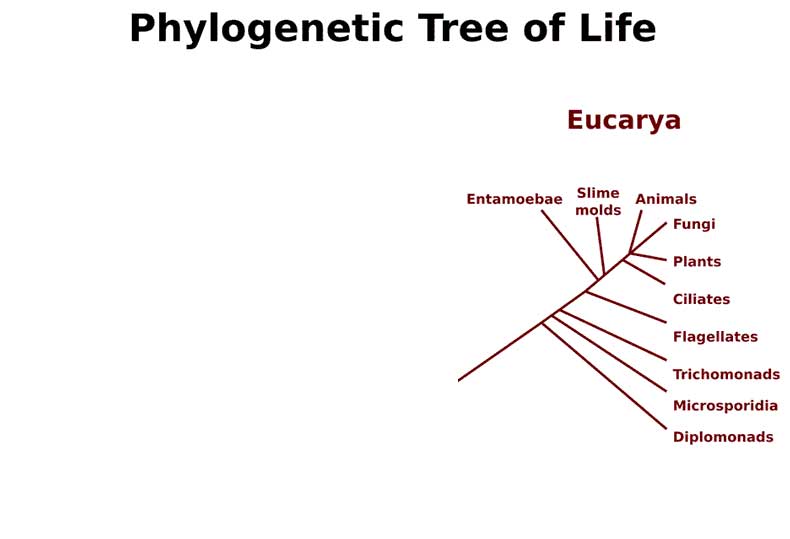
Figure 3.10: Scientists classify life according to the phylogenetic tree of life. Life is generally classified into three domains. Humans, other animals, fungi, plants and many other types of life belong to the domain Eucarya.
For more information on the Phylogenetic Tree, visit Wikipedia, URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phylogenetic_tree
(Don’t try to memorize all of the sub-classifications under the domains! For this module, they are unnecessary. We just want to be aware of the diversity of life, and have a general understanding of how scientists classify life based on observed distinctions.)